Teua lugha:
STET Triboelectrostatic separation has been used for the commercial beneficiation of coal combustion fly ash to produce a low carbon product for use as a cement replacement in concrete for nearly 20 years….
Pakua PDFF. Hrach, S. Gasiorowski, H.Guicherd
Vifaa vya ST & Teknolojia LLC (STET), 101 Avenue ya Hampton, Haja ham MA 02494 USA
CONFERENCE: Vietbuild Ho chi Minh City – Juni 2015
MANENO: Wilaya ya Ki-electrotuli, Majadiliano ya manufaa, Dry Fly Ash, Carbon Separation ABSTRACT
STET Triboelectrostatic separation has been used for the commercial beneficiation of coal combustion fly ash to produce a low carbon product for use as a cement replacement in concrete for nearly twenty years. With 18 separators in 12 coal-fired power plants across the world, Vifaa vya ST & Teknolojia ya LLC (STET) patented electrostatic separator has been used to produce over 15 Million tonnes of low carbon product.
To date, commercial beneficiation of fly ash has been performed exclusively on dry “run of station” ash. STET ya electrotuli manufaa teknolojia inapunguza maudhui ya carbon ya makaa ya mawe kuruka Ash, producing consistent, chini Carbon Ash kwa ajili ya matumizi kama mbadala kwa ajili ya saruji. Fly ash with carbon levels up to 25% have been used to produce ash with a controlled carbon level of 2 ± 0.5%. A carbon-rich product is simultaneously produced to recover the fuel value of the carbon.
UTANGULIZI
Marekani ya makaa ya mawe Ash chama (ACAA) utafiti wa mwaka wa uzalishaji na matumizi ya makaa ya mawe kuruka majivu taarifa kuwa kati ya 1966 na 2011, juu ya 2.3 billion short tons of fly ash have been produced by coal-fired utility boilers.1 Of this amount, takriban 625 tani milioni zimetumika manufaa, zaidi kwa ajili ya uzalishaji wa saruji na saruji. Hata hivyo, iliyobaki 1.7+ tani bilioni kimsingi hupatikana katika avfallsdeponierna au kujazwa ponded impoundments. While utilization rates for freshly generated fly ash have increased considerably over recent years, with current rates near 45%, takriban 40 million tons of fly ash continues to be disposed of annually. While utilization rates in Europe have been much higher than in the US, considerable volumes of fly ash have also been stored in landfills and impoundments in some European countries. An excessive amount of unburned carbon in fly ash is the most common problem. The American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) and European Standards (KISTARI 450 Category A) require that the amount of unburned carbon in fly ash, measured by loss on ignition (WA) not exceed 5% by weight. Hata hivyo, starting in the mid-1990s, installation of mandated NOx control equipment at coal-fired power plants increased the carbon (WA) content of much of the previously marketable fly ash. Further requirements to reduce NOx and other power plant emissions have resulted in the contamination of fly ash with ammonia. As a consequence, while understanding the benefits of using fly ash in concrete continues to increase, the availability of suitable quality fly ash is decreasing. Processes to economically beneficiate off-quality fly ash are thus also of increasing interest to the power and concrete industries. STET has pioneered such processes for both carbon and ammonia removal from fly ash.
TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW – FLY ASH CARBON SEPARATION
In the STET carbon separator (Kielelezo 1), the material is fed into the thin gap between two parallel planar electrodes. The particles are triboelectrically charged by interparticle
contact. The positively charged carbon and the negatively charged mineral (in freshly generated ash that has not been wetted and dried) ni kuvutia kwa electrodes kinyume. The particles are then swept up by a continuous moving belt and conveyed in opposite directions. Ukanda husonga chembe karibu na kila uchaguzi wakipanda kuelekea mwisho wa mgawanyiko. Kasi ya ukanda wa juu pia inawezesha njia za juu sana, hadi 36 tani kwa saa kwenye kitenganishi kimoja. Mwanya mdogo, high voltage field, countercurrent flow, vigorous particle-particle agitation and self-cleaning action of the belt on the electrodes are the critical features of the STET separator. Kwa kudhibiti vigezo mbalimbali vya mchakato, kama vile kasi ya ukanda, the feed point, and feed rate, the STET process produces low LOI fly ash at carbon contents of less than 1.5 kwa 4.5% from feed fly ashes ranging in LOI from 4% zaidi kwa 25%.
Mtini. 1 STET Separator
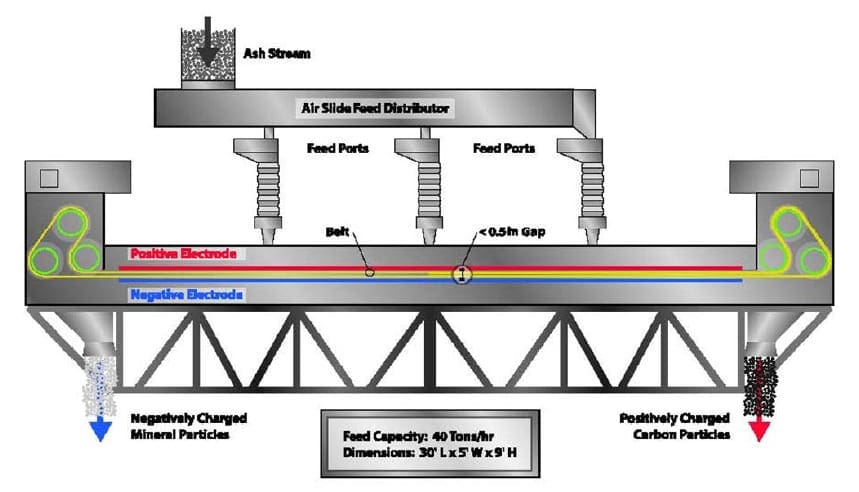
The separator design is relatively simple and compact. Mashine iliyoundwa kwa mchakato 36 tani kwa saa ni takriban 9 m (30 futi.) muda mrefu, 1.5 m (5 futi.) pana, na 2.75 m (9 futi.) juu. Ukanda na rollers kuhusishwa ni sehemu tu ya kusonga. Ya electrodes ni stationary na linajumuisha ya vifaa na muda mrefu ipasavyo. The belt is made of nonconductive plastic. The separator’s power consumption is about 1 kilowati kwa tani moja ya vifaa vya kusindika na wengi wa nguvu zinazotumiwa na motors mbili kuendesha ukanda wa.
Mchakato ni kavu kabisa, requires no additional materials other than the fly ash and produces no wastewater or air emissions. The recovered materials consist of fly ash reduced in carbon content to levels suitable for use as a pozzolanic admixture in concrete, and a high carbon fraction useful as fuel. Matumizi ya mito yote miwili ya bidhaa hutoa 100% ufumbuzi wa matatizo ya utupaji wa majivu.
RECOVERED FUEL VALUE OF HIGH-CARBON FLY ASH
In addition to the low carbon product for use in concrete, brand named ProAsh®, the STET separation process also recovers otherwise wasted unburned carbon in the form of carbon-rich fly ash, branded EcoTherm™. EcoTherm™ has significant fuel value and can easily be returned to the electric power plant using the STET EcoTherm™ Return system to reduce the coal use at the plant. When EcoTherm™ is burned in the utility boiler, the energy from combustion is converted to high pressure /high-temperature steam and then to electricity at the same efficiency as coal, typically 35%. The conversion of the recovered thermal energy to electricity in ST Equipment & Technology LLC EcoTherm™ Return system is two to three times higher than that of the competitive technology where the energy is recovered as low-grade heat in the form of hot water which is circulated to the boiler feed water system. EcoTherm™ is also used as a source of silica and alumina in cement kilns, displacing the more expensive raw materials, such as shale or bauxite, which are used in cement production. Utilizing the high carbon EcoTherm™ ash either at a power plant or a cement kiln, maximizes the energy recovery from the delivered coal, reducing the need to mine and transport additional fuel to the facilities.
STET’s Talen Energy Brandon Shores, SMEPA R.D. Kesho, NBP Belledune, RWEnpower Didcot, EDF Energy West Burton, and RWEnpower Aberthaw fly ash plants, all include EcoTherm™ Return systems. The essential components of the system are presented in Figure 2.
Mtini. 2 EcoTherm™ Return system

STET ASH PROCESSING FACILITIES
Controlled low LOI fly ash is produced with STET’s technology at twelve power stations throughout the U.S., Kanada, the U.K., Polandi, na Jamhuri ya Korea. ProAsh® fly ash
has been approved for use by over twenty state highway authorities, as well as many other specification agencies. ProAsh® has also been certified under the Canadian Standards Association and EN 450:2005 viwango vya ubora katika Ulaya. Ash processing facilities using STET technology are listed in Table 1.
Jedwali 1. STET Commercial Operations
| Matumizi / Power Station | Mahali | Mwanzo wa Kibiashara Operesheni | Facility Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duke Energy – Roxboro Station | North Carolina USA | Sept. 1997 | 2 Vitenganishi |
| Nishati ya talen - Brandon Shores Station | Maryland USA | Aprili 1999 | 2 Vitenganishi 35,000 ton storage dome. Ecotherm™ Return 2008 |
| ScotAsh (Lafarge / Scottish Power Joint Venture) - Longannet Station | Scotland UINGEREZA | Oktoba. 2002 | 1 Kitenganishi |
| Jacksonville Electric Authority - St. John’s River Power Park, FL | Florida USA | Mei 2003 | 2 Vitenganishi Coal/Petcoke blends Ammonia Removal |
| South Mississippi Electric Power Authority R.D. Kesho Station | Mississippi USA | Jan. 2005 | 1 Kitenganishi Ecotherm™ Return |
| New Brunswick Power Company Belledune Station | New Brunswick, Kanada | Aprili 2005 | 1 Kitenganishi Coal/Petcoke Blends Ecotherm™ Return |
| RWE npower Didcot Station | Uingereza UINGEREZA | Agosti 2005 | 1 Kitenganishi Ecotherm™ Return |
| Talen Energy Brunner Island Station | Pennsylvania USA | Desemba 2006 | 2 Vitenganishi 40,000 Ton storage dome |
| Tampa Electric Co. Big Bend Station | Florida USA | Aprili 2008 | 3 Vitenganishi, kupita mara mbili 25,000 Ton storage dome Ammonia Removal |
| RWE npower Aberthaw Station (Lafarge Cement UK) | Wales UINGEREZA | Septemba 2008 | 1 Kitenganishi Ammonia Removal Ecotherm™ Return |
| EDF Energy West Burton Station (Lafarge Cement UK, Cemex) | Uingereza UINGEREZA | Oktoba 2008 | 1 Kitenganishi Ecotherm™ Return |
| ZGP (Saruji ya Lafarge Poland / Ciech Janikosoda JV) | Polandi | Machi 2010 | 1 Kitenganishi |
| Korea South-East Power Yeongheung Units 5&6 | Korea Kusini | Septemba 2014 | 1 Kitenganishi Ecotherm™ Return |
| Saruji ya Lafarge Poland Warsaw | Polandi | 2016 | 1 Kitenganishi |
CONCLUSIONS
Maximizing the utilization of fly ash as a cement substitute in concrete production substantially reduces the carbon dioxide emissions associated with construction activity. Hata hivyo, pollution control systems implemented by the coal-fired power stations have resulted in a reduction of available fly ash meeting concrete-grade specifications. Further degradation of fly ash quality is expected due to further reductions in allowable gas emissions. In order to avoid loss of this valuable resource of material for concrete production as well as reduction of greenhouse gas emissions associated with concrete construction, processes for restoring the quality of the fly ash in an economic and environmentally viable way are needed.
The beneficiation of fly ash with STET processes further increases the supply of this important material. The STET beneficiation processes continue to be the most extensively applied methods to upgrade otherwise unusable fly ash to high-value materials for cement replacement in concrete. Eighteen SETT carbon separators are currently in place with over 100 machine-years of operation.
ProAsh® has found wide acceptance in the concrete industry as a premium fly ash requiring far less monitoring of air entrainment requirements due to less LOI variability than other ashes. Returning the high-carbon concentrate from the STET process to the boiler at a power plant allows recovery of the recovered carbon fuel value at an efficiency similar to coal. STET offers economical means to recover ash for high-value use that would otherwise be landfilled. Electrostatic carbon separation and Ecotherm™ return to the boiler provide a modular solution to a utility’s fly ash needs. These processes can be implemented in phases, or as a single project.
MAREJEO
[1] American Coal Ash Coal Combustion products and Use Statistics:
https://www.acaa-usa.org/Publications/Production-Use-Reports/