భాషా ఎంచుకోండి:
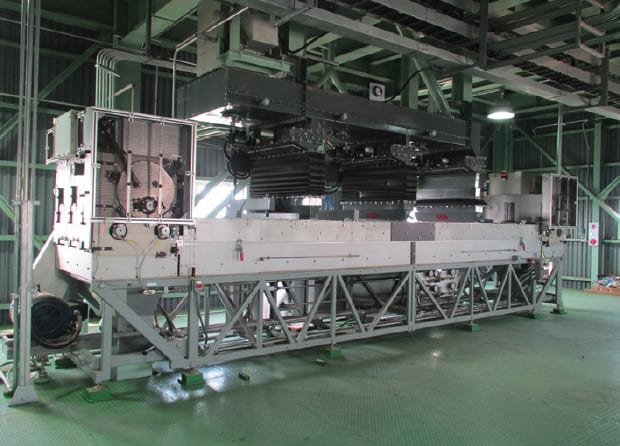
ST సామగ్రి & టెక్నాలజీ ఎస్ యూవీ (STET) ట్రైబోఎలక్ట్రోస్టాటిక్ బెల్ట్ సపరేటర్ (మూర్తి 1) నుండి రేణువుల ప్రాసెస్ ప్రదర్శించారు సామర్ధ్యం ఉంది 1995 separating Unburned carbon from fly ash minerals in coal-fired power plants in North America, Europe and Asia to produce a concrete grade Pozzolan for use as a cement substitute. 1 పైలట్ ప్లాంట్ను పరీక్ష ద్వారా, ఇన్ ప్లాంట్ డెమానిస్ట్రేషన్ ప్రాజెక్టులు మరియు/లేదా వాణిజ్య కార్యకలాపాలు, STET’s separator has demonstrated Beneficiation of many minerals including potash, బరైట్, calcite, and talc.2
Since the primary interest in this technology has been its ability to process particles less than 0.1 mm, సంప్రదాయ ఫ్రీ ఫాల్ మరియు డ్రమ్ రోల్ సపరేటర్ ల యొక్క పరిమితి, the upper particle size limit of STET’s current design has not been a focus of the development of the technology in the past. అయితే, efforts are under way to increase it by design changes. STET currently manufactures two sizes with nominal capacities of 40 మరియు 23 metric tonne per hour.
మూర్తి 1: ST సామగ్రి & Technology’s Triboelectric Belt Separator

The principles of operation of the STET separator are illustrated in Figures 2 & 3. ఎయిర్ స్లైడ్ ఫీడ్ డిస్ట్రిబ్యూటర్ మరియు ఎలక్ట్రోడ్ ల మధ్య ఉండే గ్యాప్ లోపల, పార్టుల నుంచి పార్టికల్ అభిఘాతాల ద్వారా ట్రైబోఎలక్ట్రిక్ ఎఫెక్ట్ ద్వారా కణాలు ఛార్జ్ చేయబడ్డాయి.. ఎలక్ట్రోడ్లు పాటించినప్పుడు వోల్టేజ్ ± 4 మరియు నేల ± 10kV సాపేక్ష మధ్య, యొక్క మొత్తం ఓల్టేజి వ్యత్యాసాన్ని ఇవ్వడం 8 కు 20 కెవి. నడికట్టు, ఇది నాన్-వాహక ప్లాస్టిక్ తో తయారు చేయబడింది, గురించి ఒక పెద్ద మెష్ ఉంది 60% ఓపెన్ ప్రాంతంలో. The particles can easily pass through the openings in the belt.
మూర్తి 2: Schematic of STET Separator
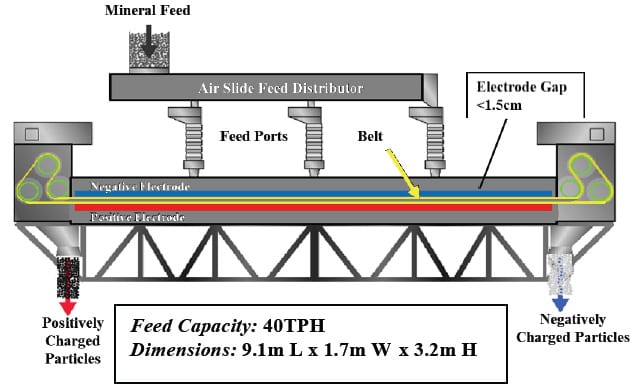
Feed Capacity: 40TPH Dimensions: 9.1m L x 1.7m W x 3.2m H
The flow patterns and particle-to-particle contact within the electrode gap that is established by the moving belt are key to the effectiveness of the separator. ఎలక్ట్రోడ్ల మధ్య గ్యాప్ లోకి ప్రవేశించిన తర్వాత రుణాత్మక ఆవేశం రేణువులను దిగువన సానుకూల ఎలక్ట్రోడ్లు విద్యుత్ రంగంలో దళాలు ఆకర్షింపబడతాయి. ధనాత్మక ఆవేశం రేణువులను రుణాత్మక ఆవేశం టాప్ ఎలక్ట్రోడ్ ఆకర్షింపబడతాయి. నిరంతర లూప్ బెల్ట్ వేగం నుండి చరరాశి 4 కు 20 m/s. The geometry of the belt cross-direction strands serves to sweep the particles of the electrodes moving them towards the proper end of the separator and back into the high shear zone between the oppositely moving sections of the belt. రేణువుల సంఖ్య డెన్సిటీ ఎలక్ట్రోడ్ల మధ్య గ్యాప్ లోపల చాలా ఎక్కువగా ఉండటం వలన (approximately one-third the volume is occupied by particles) మరియు ప్రవాహం దీనివలన ఆందోళనగా ఉంది, అక్కడ వేరు జోన్ అంతటా నిరంతరం సంభవిస్తుంది కణాలు మరియు సరైన ఛార్జింగ్ మధ్య అనేక ప్రమాదాలలో ఉన్నాయి. The counter-current flow induced by the oppositely moving belt sections and the continual re-charging and re-separation creates a countercurrent multistage separation within a single apparatus. This continuous charging and recharging of particles within the separator eliminate the need for any “charger” system prior to introducing material to the separator, thus removing a serious limitation on the capacity of electrostatic separation. ఈ విభజించడానికి అవుట్పుట్ రెండు ప్రవాహాలు ఉంది, a concentrate, and a residue, ఒక middlings ప్రవాహం లేకుండా. ఈ విభావరి యొక్క సామర్థ్యం, మిడ్ డంగ్స్ రీసైకిల్ తో స్వేచ్ఛా-పతనం వేరు యొక్క సుమారు మూడు దశల్లో సమానం అని చూపించబడింది.
మూర్తి 3: Electrode Gap of STET Belt Separator
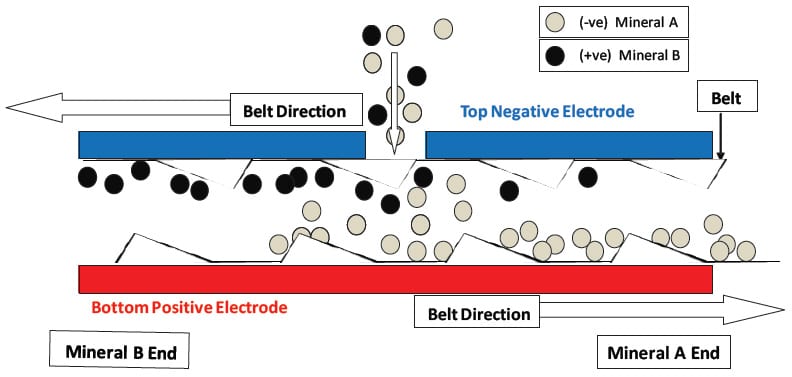
The STET separator has many process variables that enable optimization of the trade-off between product purity and recovery that is inherent in any Beneficiation process. The coarse adjustment is the feed port through which the feed is introduced to the separation chamber. The port furthest from the discharge hopper of the desired product gives the best grade but at the expense of a lower recovery. A finer adjustment is the speed of the belt. The electrode gap, which is adjustable between 9 మరియు 18 mm, and the applied voltage (±4 to ±10 kV) are also important variables. The polarity of the electrodes may be changed which aids in the separation of some materials. Pretreatment of feed material by precise control of trace moisture content (as measured by feed relative humidity) is important to achieve optimum separation results. The addition of trace amounts of charge-modifying chemical agents can also aid in optimizing the process.
పైన పేర్కొన్న విధంగా, the initial commercial application of the belt separator has been a separation of coal char from the glassy Aluminosilicate mineral from fly ash from coal-fired power plants. This technology is unique among electrostatic separators in its ability to separate fly ash, which typically has a mean particle size less than 0.02 mm. The STET separator has also been proven to effectively separate magnesite from talc, halite from kieserite and sylvite, silicates from Bart, and silicates from calcite.3 The mean particle size of all of these feed materials has been in the range of 0.02 and 0.1mm. Examples of separations for several materials are included in టేబుల్ 1.
టేబుల్ 1 – Example Separations
| ఎడబాటు | Feed | ఉత్పత్తి | రికవరీ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium Carbonate - Silicates | 9.5% Acid Insols | <1% A.I. | 89% CaCO3 |
| టాల్క్ - మాగ్నసైట్ | 58% టాల్క్ | 95% టాల్క్ | 77% టాల్క్ |
| 88% టాల్క్ | 82% టాల్క్ | ||
| Kierserite + KCl - NaCl | 11.5% K2O | 27.1% K2O | 90% K2O |
| 12.2% kieserite | 31.8% kieserite | 94% kieserite | |
| 64.3% NaCl | 14.3% NaCl | 92% NaCl reject | |
| Fly Ash Mineral - కార్బన్ | 6.3% carbon | 1.8% carbon | 88% ఖనిజ |
| 11.2% carbon | 2.1% carbon | 84% ఖనిజ | |
| 19.3% carbon | 2.9% carbon | 78% ఖనిజ |
In theory, since particle charging depends upon the triboelectric effect, any two minerals that are liberated from each other (conductor- conductor or nonconductor-conductor) can be separated by this method. Other potential applications include magnesite-quartz, feldspar-quartz, ఖనిజ ఇసుక, other potash mineral separations, మరియు
Phosphate-calcite-silica separations.
1 Bittner, J.D., Gasiorowski, ఎస్.ఏ., బుష్, T.W.,, Hrach, ఎఫ్.జె., Separation technologies’ automated fly ash beneficiation process selected for new Korean power plant, Proceedings of 2013 World of Coal Ash conference, ఏప్రిల్ 22-25, 2013. 2 Bittner, J.D., Hrach, ఎఫ్.జె., Gasiorowski, ఎస్.ఏ., Canellopoulus, L.A., Guicherd, H. Triboelectric belt separator for Beneficiation of fine minerals, SYMPHOS 2013 – 2nd International Symposium on Innovation and Technology for the Phosphate Industry. Proceed Engineering, సం. 83 PP 122-129, 2014. 3 Bittner, J.D., ఫ్లిన్, K.P., Hrach, ఎఫ్.జె., Expanding applications in dry Triboelectric separation of minerals, XXVII అంతర్జాతీయ మినరల్ ప్రోసెసింగ్ కాంగ్రెస్ ప్రొసీడింగ్స్ - IMPC 2014, శాంటియాగో, చిలీ, Oct 20 - 24, 2014.