Piliin ang Wika:
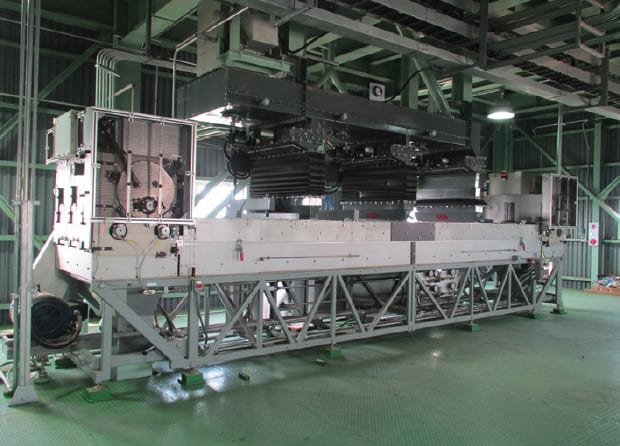
Kagamitang ST & Technology LLC ni (STET) Triboelectrostatic belt separator (pigura 1) may nagpakita ng kakayahan upang i-proseso fine particle mula 1995 na naghihiwalay Unburned carbon mula sa fly ash mineral sa karbon-fired halaman kapangyarihan sa Hilagang Amerika, Europe and Asia to produce a concrete grade Pozzolan for use as a cement substitute. 1 Sa pamamagitan pilot plant testing, in-plant demonstration proyekto at / o komersyal na operasyon, STET’s separator has demonstrated Beneficiation of many minerals including potash, barite, calcite, at talc.2
Dahil ang pangunahing interes sa teknolohiya na ito ay ang kakayahan upang i-proseso particle mas mababa sa 0.1 mm, ang limitasyon ng maginoo libreng-pagkahulog at drum roll panghiwalay, the upper particle size limit of STET’s current design has not been a focus of the development of the technology in the past. gayunman, efforts are under way to increase it by design changes. STET kasalukuyang mga paninda dalawang mga laki na may nominal capacities ng 40 at 23 panukat tonelada kada oras.
pigura 1: Kagamitang ST & Teknolohiya triboelectric Belt Separator

Ang prinsipyo ng operasyon ng STET separator ay isinalarawan sa Figure 2 & 3. Ang mga particle ay nasingil ayon sa triboelectric epekto sa pamamagitan ng maliit na butil-to-maliit na butil banggaan sa hangin slide feed distributor at sa loob ng agwat sa pagitan ng mga electrodes. Ang inilapat boltahe sa electrodes ay sa pagitan ± 4 at ± 10kV kamag-anak sa lupa, pagbibigay ng isang kabuuang boltahe pagkakaiba ng 8 sa 20 kV. ang sinturon, na kung saan ay ginawa ng isang di-pagsasagawa plastic, ay isang malaking mesh na may tungkol sa 60% bukas na lugar. Ang mga particle ay madaling pumasa sa pamamagitan ng openings sa belt.
pigura 2: Eskematiko ng STET Separator
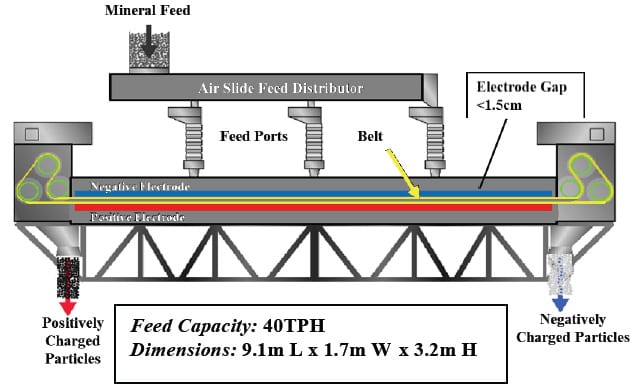
feed Kapasidad: 40TPH Mga dimensyon: 9.1m L x 1.7m W x 3.2m H
The flow patterns and particle-to-particle contact within the electrode gap that is established by the moving belt are key to the effectiveness of the separator. Sa pagpasok sa puwang sa pagitan ng mga electrodes ng mga negatibong sisingilin particle ay naaakit sa pamamagitan ng mga de-kuryenteng puwersa field sa ilalim positibong elektrod. Ang positibo sisingilin particle ay akit sa mga negatibong sisingilin top elektrod. Ang bilis ng tuloy-tuloy na loop belt ay variable mula sa 4 sa 20 MS. The geometry of the belt cross-direction strands serves to sweep the particles of the electrodes moving them towards the proper end of the separator and back into the high shear zone between the oppositely moving sections of the belt. Dahil ang maliit na butil number density ay kaya mataas na sa loob ng agwat sa pagitan ng mga electrodes (approximately one-third the volume is occupied by particles) at ang daloy ay masigla agitated, maraming mga collisions sa pagitan ng mga particle at optimal charging nangyayari patuloy na sa buong paghihiwalay zone. The counter-current flow induced by the oppositely moving belt sections and the continual re-charging and re-separation creates a countercurrent multistage separation within a single apparatus. This continuous charging and recharging of particles within the separator eliminate the need for any “charger” system prior to introducing material to the separator, thus removing a serious limitation on the capacity of electrostatic separation. Ang output ng separator na ito ay dalawang batis, a concentrate, at isang residue, walang midling stream. Ang kahusayan ng separator ito ay nai-ipinapakita na maging katumbas ng humigit-kumulang tatlong yugto ng libreng-pagkahulog paghihiwalay sa midling recycle.
pigura 3: Elektrod Gap of STET Belt Separator
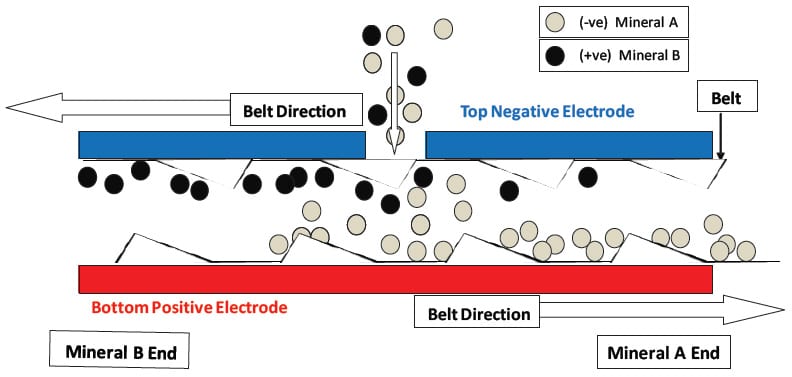
The STET separator has many process variables that enable optimization of the trade-off between product purity and recovery that is inherent in any Beneficiation process. The coarse adjustment is the feed port through which the feed is introduced to the separation chamber. The port furthest from the discharge hopper of the desired product gives the best grade but at the expense of a lower recovery. Ang isang mas pinong adjustment ay ang bilis ng belt. The electrode gap, na kung saan ay madaling iakma sa pagitan 9 at 18 mm, at ang inilapat boltahe (± 4 sa ± 10 kV) are also important variables. Ang polarity ng electrodes ay maaaring baguhin kung saan aid sa paghihiwalay ng ilang mga materyales. Pretreatment of feed material by precise control of trace moisture content (bilang sinusukat sa pamamagitan ng feed na kamag-anak halumigmig) is important to achieve optimum separation results. The addition of trace amounts of charge-modifying chemical agents can also aid in optimizing the process.
Tulad nang nakalagay sa itaas, the initial commercial application of the belt separator has been a separation of coal char from the glassy Aluminosilicate mineral from fly ash from coal-fired power plants. This technology is unique among electrostatic separators in its ability to separate fly ash, na karaniwang may isang mean na butil laki ng mas mababa sa 0.02 mm. The STET separator has also been proven to effectively separate magnesite from talc, halite from kieserite and sylvite, silicates mula sa Bart, and silicates from calcite.3 The mean particle size of all of these feed materials has been in the range of 0.02 at 0.1mm. Mga halimbawa ng mga separations para sa ilang mga materyales ay kasama sa mesa 1.
mesa 1 - Halimbawa Separations
| paghihiwalay | Magpakain | produkto | pagbawi |
|---|---|---|---|
| calcium Carbonate - Silicates | 9.5% Acid Insols | <1% A.I. | 89% CaCO3 |
| mika - magnesite | 58% mika | 95% mika | 77% mika |
| 88% mika | 82% mika | ||
| Kierserite + KCl - NaCl | 11.5% K2O | 27.1% K2O | 90% K2O |
| 12.2% kieserite | 31.8% kieserite | 94% kieserite | |
| 64.3% NaCl | 14.3% NaCl | 92% NaCl reject | |
| Fly Ash Mineral - karbon | 6.3% karbon | 1.8% karbon | 88% mineral |
| 11.2% karbon | 2.1% karbon | 84% mineral | |
| 19.3% karbon | 2.9% karbon | 78% mineral |
sa basal, since na butil-charge ay depende sa triboelectric epekto, anumang dalawang mineral na liberated mula sa bawat isa (konduktor- konduktor o nonconductor-konduktor) maaaring paghiwalayin ng ang paraan na ito. Iba pang mga potensyal na mga aplikasyon ay kinabibilangan ng magnesite-kuwarts, feldspar-kuwarts, mineral sands, iba pang potash mineral separations, at
Phosphate-calcite-silica separations.
1 Bittner, J.D., Gasiorowski, S.A., Bush, T.W.,, Hrach, F.J., Separation technologies’ automated fly ash beneficiation process selected for new Korean power plant, paglilitis ng 2013 World of Coal Ash conference, Abril 22-25, 2013. 2 Bittner, J.D., Hrach, F.J., Gasiorowski, S.A., Canellopoulus, L.A., Guicherd, H. Triboelectric belt separator for Beneficiation of fine minerals, SYMPHOS 2013 – 2nd International Symposium on Innovation and Technology for the Phosphate Industry. magpatuloy Engineering, Vol. 83 PP 122-129, 2014. 3 Bittner, J.D., Flynn, K.P., Hrach, F.J., Ang pagpapalawak ng mga application sa dry triboelectric paghihiwalay ng mineral, Paglilitis ng XXVII International Mineral Processing Congress - iMPC 2014, Santiago, Tsile, Oktubre 20 - 24, 2014.